El llamado Escudo Azul (Blue Shield) es una organización internacional no gubernamental sin ánimo de lucro destinada a proteger el patrimonio tangible e intangible.

Este mecanismo surge como respuesta a la necesidad de proteger el patrimonio de conflictos armados. Tras los ataques y pérdidas durante la I y II Guerra Mundial, la UNESCO organizó, en 1954, la Convención de la Haya (Países Bajos). Fue el primer tratado dedicado a la protección del patrimonio cultural en caso de conflicto armado, estableciendo también medidas preventivas en tiempos de paz. Además, cada Alta Parte Contratante tiene el compromiso de impedir la exportación de bienes culturales de un territorio ocupado, así como la obligación de la devolución de los mismos tras la finalización de un conflicto, impidiendo así, la retención de bienes culturales como daño de guerra.
La junta directiva de este organismo, Blue Shield International Board, presenta en sus estatutos los siguientes objetivos:
- Protección proactiva del patrimonio tangible e intangible, natural y cultural tras conflictos armados y desastres ambientales.
- Formación y capacitación profesional para prevenir y responder a daños sobre el patrimonio cultural.
- Asistencia en zonas con evidencia de destrucción del patrimonio cuando no existe la declaración oficial de conflicto.
- Asesoramiento para la mejora de la legislación internacional en términos de protección patrimonial.
- Prevención del tráfico ilícito.
El 5 de abril de 2022, la UNESCO pedía el uso de Escudos Azules en Ucrania para proteger su patrimonio, preocupada principalmente por 28 lugares considerados de especial interés cultural. En 1991 y 1992, este recurso ya fue utilizado durante la Guerra de Croacia para garantizar la perdurabilidad de sus edificios históricos. Además, cabe mencionar que, en 2016, la Corte Penal Internacional procesó, por primera vez en la historia, a una persona por atentar contra el patrimonio cultural.
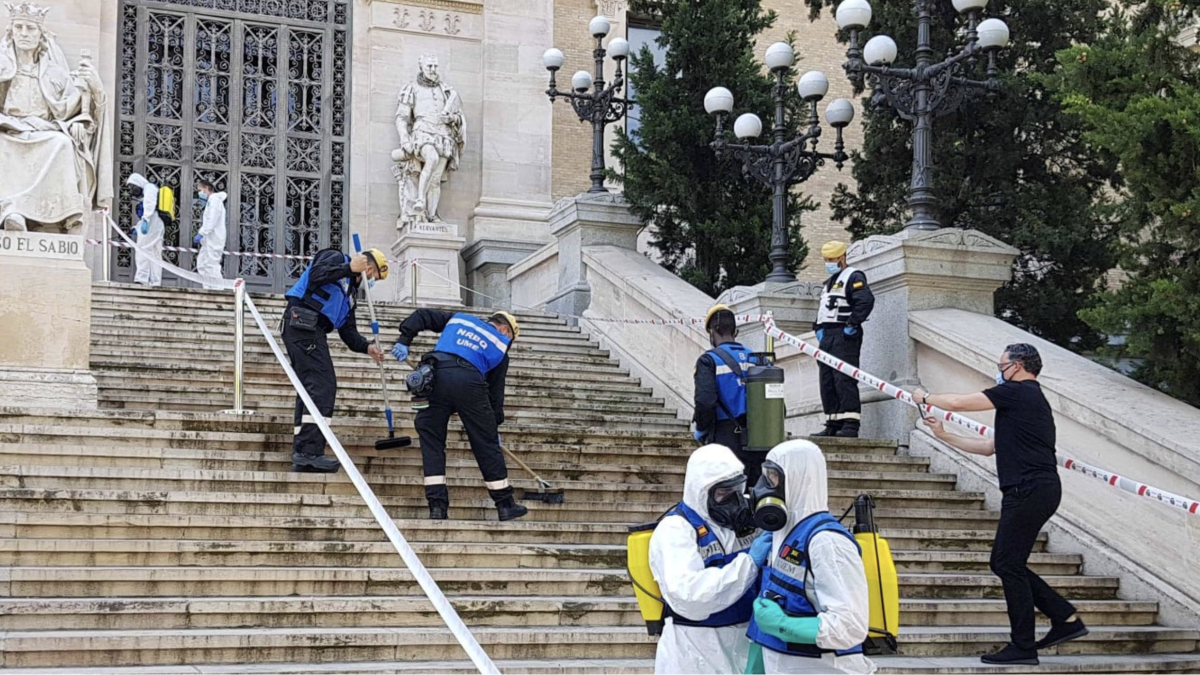

En España, se creó el Comité Escudo Azul el 14 de noviembre de 2013, coincidiendo con la elaboración de los planes de coordinación y emergencias del patrimonio gracias al Plan Nacional de Emergencias y Gestión de Riesgos (PNEGR).
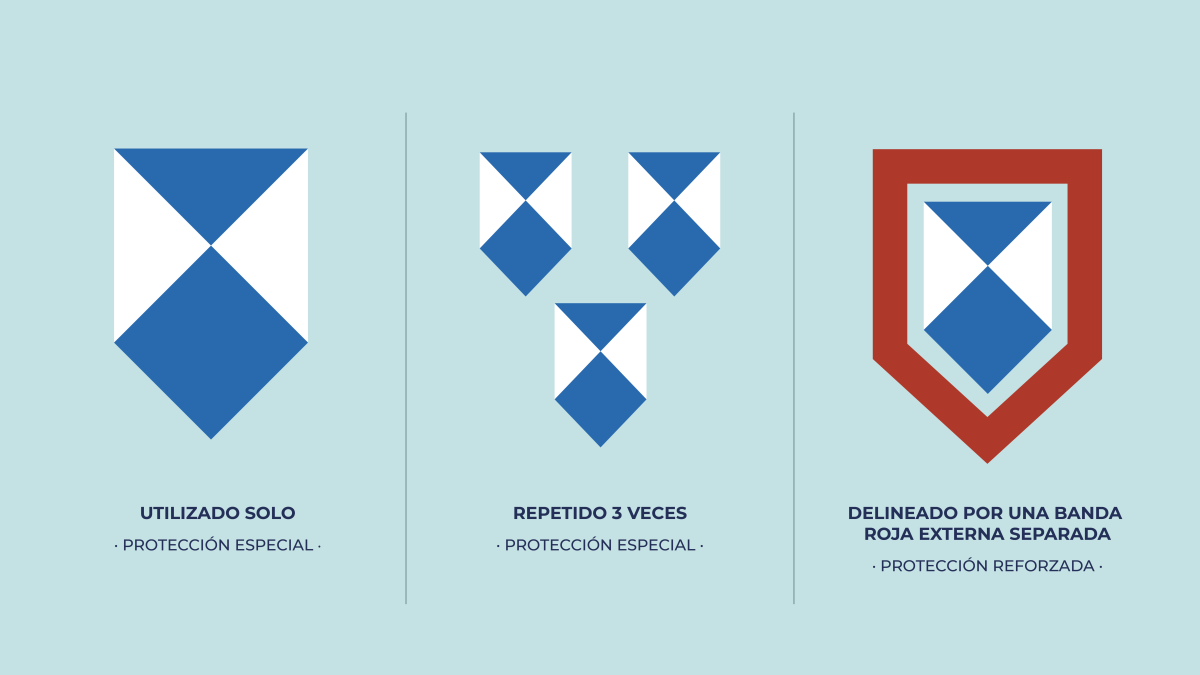
Este emblema bicolor pretende marcar un límite que permita conservar aquello que nos representa y blindar nuestros monumentos históricos de situaciones como el conflicto armado.
__
BLUE SHIELD: A DISTINCTIVE EMBLEM FOR HERITAGE PROTECTION
The Blue Shield is an international non-governmental, non-profit organization aimed at protecting tangible and intangible heritage.
This mechanism arose in response to the need to protect heritage from armed conflict. Following the attacks and losses during World War I and II, UNESCO organized, in 1954, the Haya Convention (Netherlands). It was the first treaty dedicated to the protection of cultural heritage in the event of armed conflict, establishing also preventive measures in peacetime. In addition, each High Contracting Party has the commitment to prevent the export of cultural property from an occupied territory, as well as the obligation to return it after the end of a conflict, thus preventing the retention of cultural property as war damage.
The board of directors of this organization, Blue Shield International Board, presents in its statutes the following objectives:
- Proactive protection of tangible and intangible, natural and cultural heritage following armed conflicts and environmental disasters.
- Professional training and capacity building to prevent and respond to damage to cultural heritage.
- Assistance in areas with evidence of heritage destruction when there is no official declaration of conflict.
- Advice for the improvement of international legislation in terms of heritage protection.
- Prevention of illicit trafficking.
On April 5th, 2022, UNESCO called for the use of Blue Shields in Ukraine to protect its heritage, mainly concerned about 28 sites considered to be of special cultural interest. In 1991 and 1992, this resource was already used during the Croatian War to ensure the durability of its historic buildings. In addition, it is worth mentioning that, in 2016, the International Criminal Court prosecuted, for the first time in history, a person for attacking cultural heritage.
In Spain, the Blue Shield Committee was created on November 14, 2013, coinciding with the development of heritage coordination and emergency plans thanks to the National Emergency and Risk Management Plan (PNEGR).
This two-color emblem is intended to mark a boundary that allows us to preserve what represents us and shield our historic monuments from situations such as armed conflict.
__
